AUTHOR : SIMON DRAVIS
Introduction
The forex market[1] offers tremendous opportunities for profit, but it also comes with significant risks. In India, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) plays a crucial role in regulating and overseeing the financial markets, including forex trading. To protect investors and ensure the integrity of the market, SEBI has implemented a set of guidelines for forex trading. These guidelines aim to foster transparency, fairness, and security in the forex trading environment.
In this article, we will explore the SEBI forex trading[2] guidelines, their importance, and how they affect traders in India. Additionally, we will cover common questions about the regulations and provide insight into how traders can comply with them.
What is SEBI?
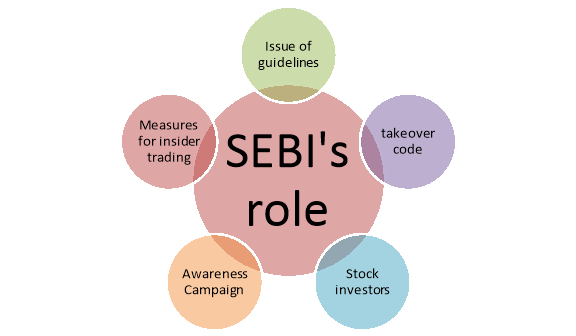
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the regulatory authority responsible for overseeing the functioning of the securities and commodity markets in India. SEBI’s main objectives include:
- Regulating Market Activities: SEBI ensures that the securities markets[3] function in a fair, efficient, and transparent manner.
- Protecting Investors: SEBI strives to protect the interests of investors by enforcing regulations and monitoring market activities.
- Promoting Financial Literacy: SEBI works to increase financial awareness among investors and traders to make informed decisions.
While SEBI primarily focuses on securities and stock market activities, its oversight extends to the forex market in India, particularly when it involves the trading of derivatives and other financial instruments[4].
Forex Trading in India: SEBI’s Role
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) primarily regulates forex trading[5] in India under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA). However, SEBI’s role is also crucial when it comes to certain forex instruments, such as currency futures and options.
Currency Derivatives and SEBI’s Guidelines
In 2008, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) introduced guidelines for currency derivatives to regulate the trading of currency futures and options on exchanges. These guidelines specifically apply to the trading of derivatives contracts that involve foreign currencies, such as USD/INR, EUR/INR, and GBP/INR, on recognized stock exchanges like the NSE and BSE.
Under SEBI’s supervision, currency futures and options have become popular among Indian traders, offering a regulated platform for currency speculation. Here are some of the key guidelines governing forex trading in India:
1. Recognized Exchanges and Platforms
Forex trading in India occurs only on recognized exchanges, and traders cannot engage in off-exchange forex trading. SEBI-approved exchanges such as the National Stock Exchange (NSE), Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), and Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX) are the only legal platforms for trading currency derivatives.
These exchanges offer a transparent and regulated environment for buying and selling currency futures and options contracts. Traders can access them through brokers registered with SEBI.
2. Margin Requirements and Leverage
SEBI has established strict guidelines on margin requirements and leverage for currency trading. The guidelines help protect traders from excessive risks, especially when dealing with highly volatile currency markets.
- Margin Requirements: SEBI mandates that traders maintain a minimum margin to open positions in currency derivatives. The margin requirements ensure that traders have sufficient capital to cover potential losses.
- Leverage: SEBI sets limits on the leverage that brokers can offer to traders. In the case of currency futures, the leverage ratio is generally limited to 1:10, meaning that a trader can control a position that is ten times larger than the capital they have invested.
This ensures that traders do not take on excessive risk when entering the forex market and helps prevent excessive speculation that could destabilize the market.
3. Eligibility Criteria for Traders
SEBI has set eligibility criteria for individuals wishing to trade currency derivatives in India. These criteria ensure that only financially literate and capable traders engage in forex trading, reducing the risks associated with inexperienced participants.
- KYC (Know Your Customer) Compliance: Traders must complete the KYC process before opening an account with a registered broker. This process ensures that traders meet the necessary financial and identity checks.
- Age Requirement: To engage in forex trading, individuals must be at least 18 years old.
- Financial Requirements: Traders must meet certain financial criteria to participate in forex trading, which includes having a minimum deposit to cover margin requirements.
4. Risk Disclosure and Investor Education
One of SEBI’s key objectives is to protect retail investors by promoting financial literacy. As part of this, SEBI mandates that brokers provide clear risk disclosures to traders before they start trading in currency derivatives. This ensures that traders understand the risks involved and are well-prepared for potential losses.
- Risk Warnings: Brokers are required to provide risk warnings to traders, explaining the risks involved in trading currency derivatives, including the potential for significant losses.
- Investor Education: SEBI also encourages brokers to offer investor education programs and resources to help traders make informed decisions in the forex market.
5. Trade Settlement and Reporting
To maintain transparency and accountability, SEBI requires that all forex trades on recognized exchanges be settled in cash. Traders do not physically exchange foreign currencies; instead, they settle their positions in Indian Rupees (INR) based on the profit or loss made from the trade.
Additionally, brokers are required to report all transactions to the exchange and provide detailed statements to their clients, ensuring complete transparency in the trading process.
6. Prohibited Activities
SEBI has clearly defined activities that are prohibited in forex trading:
- Off-Market Forex Trading: Trading in foreign exchange outside of recognized exchanges is illegal in India. Off-market transactions are unregulated and expose traders to higher risks, including fraud and market manipulation.
- Speculation in Foreign Exchange: SEBI allows currency derivatives trading, but speculative trading without proper risk management or hedging strategies is discouraged.
- Unregistered Brokers: Traders must only engage with brokers who are registered with SEBI and authorized by recognized exchanges. Dealing with unregistered brokers is a violation of Indian regulations.
Impact of SEBI’s Forex Trading Guidelines
The implementation of SEBI’s guidelines has had several positive effects on the Indian forex market:
- Market Integrity: By regulating the forex market, SEBI has helped maintain market integrity and transparency, reducing the potential for fraud and manipulation.
- Investor Protection: SEBI’s focus on investor education and risk disclosure ensures that traders are aware of the risks involved in forex trading and are not taken advantage of by unscrupulous brokers.
- Market Liquidity: The introduction of currency derivatives trading on recognized exchanges has enhanced market liquidity, allowing traders to execute large orders without significant slippage.
Conclusion
SEBI’s forex trading guidelines are designed to ensure that the forex market in India operates in a transparent, fair, and regulated environment. By adhering to these guidelines, traders can protect themselves from excessive risk and make informed trading decisions. While forex trading can be highly rewarding, it is crucial to understand and follow SEBI’s regulations to ensure compliance and mitigate potential risks.
By focusing on regulated platforms, maintaining adequate margin levels, and adhering to the risk management practices set by SEBI, traders can navigate the forex market with greater confidence and security.
FAQs
1. Can Indian traders trade in forex with foreign brokers? No, Indian traders are only allowed to trade forex through SEBI-registered brokers on recognized exchanges. Trading with foreign brokers outside India is prohibited.
2. What are currency derivatives, and how are they regulated by SEBI? Currency derivatives are financial contracts based on the future value of a currency pair. SEBI regulates currency futures and options traded on recognized exchanges in India, ensuring compliance with margin requirements, risk disclosures, and settlement practices.
3. What is the margin requirement for forex trading in India? The margin requirement for trading currency futures in India is set by SEBI, with leverage usually limited to 1:10. This means that traders must maintain a minimum margin to open a position, ensuring they can cover potential losses.
4. How can I ensure compliance with SEBI’s forex trading guidelines? To comply with SEBI’s guidelines, trade on recognized exchanges, use SEBI-registered brokers, and complete KYC requirements. Always read the risk disclosures provided by your broker and manage your positions responsibly.
5. Can I trade in forex without a broker in India? No, trading forex without a registered broker is illegal in India. You must use a SEBI-approved broker to access recognized exchanges for forex trading.





