AUTHOR : LISA WEBB
Introduction
Forex trading has evolved into one of the most popular financial markets globally, and India is no exception. The foreign exchange market offers a vast range of opportunities for traders, allowing them to engage in currency pairs from around the world. While it can be a complex and fast-moving market, one of the most commonly used strategies for beginners and seasoned traders alike is trading with moving averages. We will explore how moving averages can be effectively applied in forex trading, focusing on the Indian market. What is a currency correlation in Forex?
What Are Moving Averages?
A moving average[1] is a technical indicator that smooths price data to create a trend-following indicator. It helps traders understand the general direction of the market

- Simple Moving Average (SMA): This is the most straightforward moving average, calculated by adding up the closing prices over a specific number of periods and Simple Moving Average,[2] then dividing the sum by the total number of periods.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): This moving average gives more weight to the most recent price data, making it more sensitive to price movements. Exponential Moving Average [3] It is often preferred by traders looking for quicker signals.
- Weighted Moving Average (WMA): Similar to the EMA, the WMA assigns different weights to each data point in the moving average calculation, Weighted Moving Average[4] but with a more linear approach to weighting.
Why Use Moving Averages in Forex Trading?
Moving averages provide clear signals and can be used to identify potential entry and exit points for trades. Here’s why moving averages are so effective:
- Trend Identification: Moving averages can easily highlight the prevailing market trend—whether it’s bullish, bearish, or neutral. A price above a moving average often indicates an uptrend.
- Smoothing Volatility: The forex market is highly volatile, especially when trading currencies[5] like the Indian Rupee (INR) against other major currencies like the US Dollar (USD) or Euro (EUR).
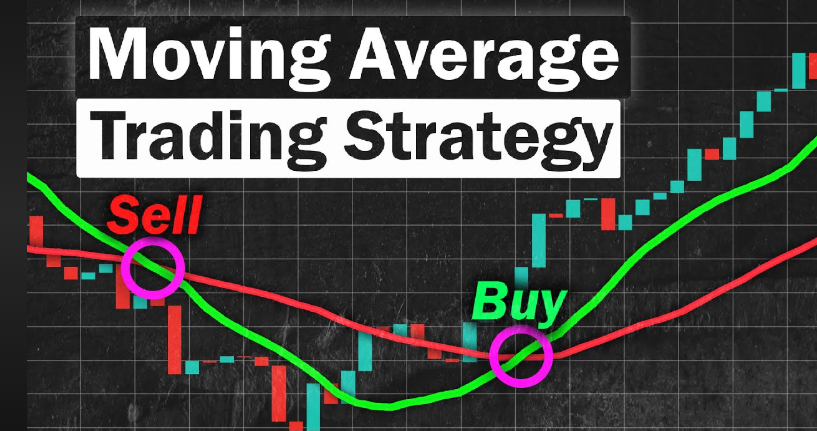
- Crossovers: One of the most popular strategies using moving averages is the crossover strategy. This occurs when a short-term moving average crosses above or below a long-term moving average.
How to Use Moving Averages in Forex Trading in India
Moving Average Crossovers
The moving average crossover strategy involves using two moving averages with different periods, typically a short-term moving average (e.g., 50 period) and a long-term moving average (e.g., 200 period). When the short-term moving average crosses above the long-term moving average.
Traders in India can use this strategy with currency pairs involving the Indian rupee, such as USD/INR or GBP/INR. For instance, if the 50-period EMA crosses above the 200-period EMA in a pair like USD/INR.
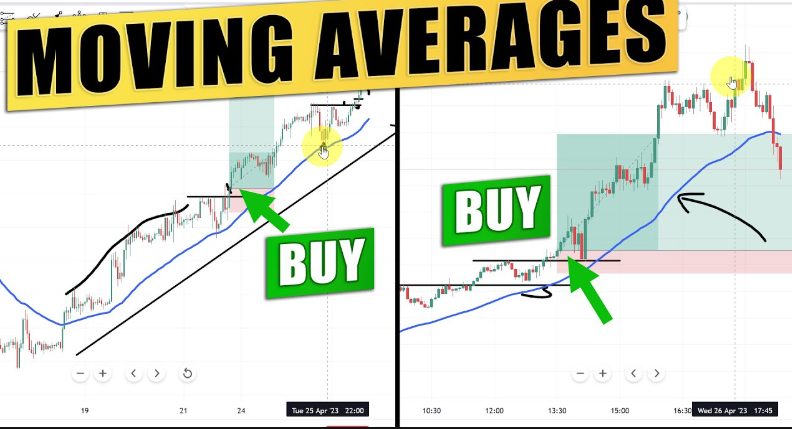
Support and Resistance Levels
When the price of a currency pair is in an uptrend, the moving average can provide support, as the price tends to bounce off the moving average. Similarly, in a downtrend, the moving average may act as a resistance level, with the price struggling to rise above it.
For example, if the INR/USD pair is rising and the 50-period moving average consistently holds the price above it, traders can use this moving average as a support level, entering buy positions when the price pulls back to the moving average.
Filtering Out False Signals
In forex trading, especially in a volatile market like the Indian forex market, false signals can occur frequently. Moving averages help traders filter out these noise-induced signals by confirming the overall trend. For instance, using a longer moving average (such as the 200-period SMA) helps to confirm that a trend is in place, reducing the likelihood of reacting to short-term price swings.
Timeframe Selection for Indian Forex Markets
The Indian forex market operates in the same global hours as the rest of the world, but Indian traders may face different liquidity conditions based on their time zone. It’s important to choose the right timeframes for moving averages depending on the type of trading you are involved in.
For day traders in India, shorter timeframes like 5-minute, 15-minute, or hourly charts might be suitable, with moving averages like the 10-period and 50-period EMAs being useful. For swing traders or position traders.
Common Challenges and Tips for Indian Traders

- High Volatility: The forex market can be highly volatile, especially when trading the INR against global currencies. Be cautious when trading during times of high volatility.
- Risk Management: No strategy, including moving averages, is foolproof. Always use stop losses, manage your position size, and ensure you have a risk-reward ratio in place to minimize potential losses.
- Combining with Other Indicators: Moving averages are powerful, but they work best when combined with other indicators such as Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, or MACD for confirmation and to avoid false signals.
Conclusion
Forex trading with moving averages is a highly effective strategy that helps Indian traders navigate the dynamic currency markets. Moving averages simplify complex price movements, allowing traders to spot trends, identify potential entry/exit points, and make informed decisions. By using moving averages strategically, traders can enhance their chances of success in the forex market, whether they are trading INR pairs or international currency pairs.
FAQs
What is Forex trading with moving averages in India?
Forex trading involves buying and selling currencies, using moving averages to analyze price trends.
How do moving averages help in Forex trading?
Moving averages smooth out price data to identify trends and entry/exit points for trades.
Are moving averages reliable in Forex trading?
Moving averages are useful but should be combined with other tools for better accuracy.
Can I trade Forex with moving averages in India?
Yes, Indian traders can trade Forex using moving averages on regulated platforms.
How can I practice Forex trading with moving averages?
You can practice on demo accounts provided by Forex brokers without real money.