AUTHOR : BERRY
INTRODUCTION
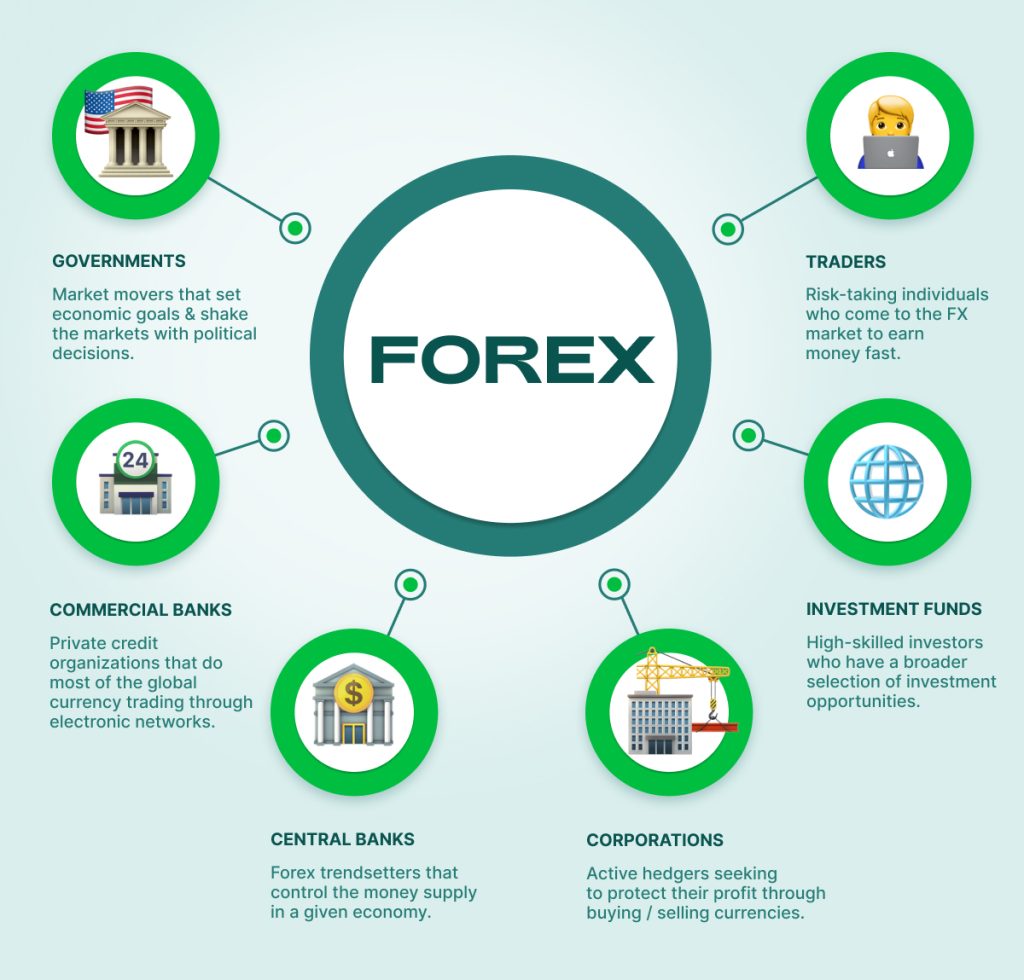
In the world of Forex trading, understanding central bank[1] interventions is essential for traders, especially in emerging markets like India. Central banks play a significant role in shaping the currency markets by managing exchange rates, controlling inflation, and fostering economic stability. This article delves into the strategies of central bank interventions in the Forex market[2] specifically focusing on India, where such interventions can have a notable impact due to the country’s economic position and trade relations.
What is Central Bank Intervention in Forex Markets?
Central bank intervention in Forex markets refers to the actions taken by a country’s central bank to influence the value of its currency in the global market[3]. These interventions can be either direct or indirect and are usually aimed at stabilizing the currency, controlling inflation, or supporting economic policy objectives.
There are two primary types of interventions:

- Direct Intervention: This involves the buying or selling of the country[4]’s own currency in the open market to adjust its value. This type of intervention is often used when the currency is fluctuating too wildly or is perceived to be undervalued or overvalued.
- Indirect Intervention: Central banks [5]use tools like interest rate changes or adjusting reserve requirements to influence the currency indirectly. These measures can alter investor behavior, leading to changes in the currency’s value over time.
Central Bank’s Role in India’s Forex Market
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central authority responsible for managing India’s monetary and Forex policies. The RBI intervenes in the Forex market mainly to:
- Stabilize the Rupee (INR): India’s currency, the Indian Rupee (INR), is susceptible to fluctuations due to factors such as inflation, trade imbalances, and foreign investments. The RBI monitors the INR’s value closely and may intervene when it feels that the rupee is becoming too volatile or misaligned with India’s economic fundamentals.
- Control Inflation: A weaker rupee can drive up the cost of imports, leading to inflation. By stabilizing the currency, the RBI can help mitigate inflationary pressures, which is crucial for maintaining the purchasing power of Indian consumers.
- Encourage Economic Growth: Stable exchange rates foster a favorable environment for foreign investments, which can drive economic growth. The RBI’s interventions can support this by managing the rupee’s volatility and ensuring that India remains an attractive destination for global investors.
How Do Central Banks Intervene in the Forex Market?

There are several strategies that central banks, including the RBI, can use to influence the Forex market. These strategies can vary based on the country’s economic conditions and policy objectives. Some common methods of intervention are:
1. Foreign Exchange Reserves Management
Central banks, including the RBI, hold large reserves of foreign currencies to manage exchange rate fluctuations. By using these reserves to buy or sell currencies in the open market, they can influence the currency’s value. For instance, if the rupee is weakening and the RBI wants to prevent further depreciation, it may sell U.S. dollars from its reserves to buy rupees, thereby increasing demand for the local currency and supporting its value.
2. Interest Rate Adjustments
Interest rates are one of the most powerful tools central banks use to influence the currency. When the RBI changes interest rates, it directly affects the return on investments in the country. Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, leading to increased demand for the rupee, which can cause its value to appreciate. Conversely, lowering interest rates can reduce demand for the currency and lead to depreciation.
3. Currency Pegs and Bands
Some countries peg their currency to a more stable foreign currency, such as the U.S. dollar. While India does not officially peg the rupee, the RBI sometimes intervenes to prevent the rupee from deviating too far from a predetermined range or Forex trading central bank intervention strategies India “band” of exchange rates. This kind of intervention helps maintain stability and investor confidence.
4. Open Market Operations (OMOs)
The RBI also conducts open market operations to influence the liquidity of the currency in the market. Through OMOs, the RBI buys or sells government securities to inject or absorb liquidity from the banking system. These operations help maintain the stability of the money supply, which, in turn, influences exchange rates.
5. Forward Contracts and Derivatives
To protect against currency risks, central banks may use forward contracts and other derivatives. These financial instruments allow the RBI to lock in exchange rates for future transactions, Forex trading central bank intervention strategies India thereby stabilizing the currency and reducing uncertainty for investors.
Factors Influencing Central Bank Interventions in India
Several factors guide the RBI’s decision to intervene in the Forex market:
1. Global Economic Conditions
India is part of the global economy, and fluctuations in international trade, commodity prices, and global interest rates can impact the rupee. For example, if global oil prices rise sharply, India’s trade deficit increases because of higher Forex trading central bank intervention strategies India import costs. The RBI may intervene in such situations to prevent excessive depreciation of the rupee.
2. Inflation Rates
High inflation erodes the value of the rupee, making imports more expensive. To curb inflationary pressures, the RBI may intervene to support the currency. Additionally, inflation data can influence the central bank’s interest rate decisions, which in turn impacts the currency.
3. Capital Flows
India’s financial markets are influenced by both foreign direct investment (FDI) and foreign portfolio investment (FPI). A sudden outflow of foreign capital can lead to a sharp depreciation of the rupee. In such cases, the RBI might intervene by using its foreign exchange reserves to stabilize the currency.
4. Monetary Policy Goals
The RBI’s intervention strategies also align with its broader monetary policy goals, which include managing inflation, supporting economic growth, and maintaining financial stability. These policies often involve adjusting interest rates or liquidity measures to influence the currency market.
Impact of Central Bank Interventions on Forex Trading in India
Central bank interventions can significantly affect Forex trading in India. Traders and investors must be aware of these actions to adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Short-Term Market Movements: Interventions can lead to sharp, short-term changes in the currency’s value. Traders who can anticipate or react quickly to these interventions may benefit from profitable opportunities.
- Market Volatility: While interventions are designed to reduce volatility, they can sometimes create uncertainty, particularly if traders perceive the actions as inconsistent or overly aggressive.
- Long-Term Trends: Prolonged interventions may alter the long-term trend of the currency. For example, consistent support of the rupee can lead to an appreciation in the long run, while frequent interventions to prevent appreciation can keep the currency weaker.
Conclusion
Central bank interventions play a critical role in shaping the Forex market in India. By using tools like foreign exchange reserves, interest rate adjustments, and open market operations, the Reserve Bank of India works to stabilize the currency, control inflation, and support economic growth. Understanding these strategies and their effects on the market can help Forex traders make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of India’s currency markets.
FAQ
- What is central bank intervention in Forex trading in India? Central bank intervention in Forex trading refers to the actions taken by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to influence the value of the Indian Rupee (INR) in the global market. This can include direct actions like buying or selling currency or indirect methods such as adjusting interest rates to stabilize or influence the rupee’s value.
- Why does the RBI intervene in the Forex market? The RBI intervenes to achieve several goals, including stabilizing the rupee, controlling inflation, managing India’s foreign exchange reserves, and encouraging favorable economic conditions. By influencing the value of the rupee, the RBI ensures that currency fluctuations do not negatively impact the economy or trade.
- What tools does the RBI use for Forex intervention? The RBI uses several tools, such as foreign exchange reserves, interest rate changes, open market operations (OMOs), and forward contracts. These strategies help manage liquidity, curb excessive volatility, and maintain a stable exchange rate for the rupee.
- How does central bank intervention affect Forex traders in India? For Forex traders, the RBI’s actions can cause short-term volatility in the INR. Traders who monitor and understand RBI intervention strategies can potentially profit from currency fluctuations caused by these interventions. However, interventions may also make the market unpredictable, creating challenges for traders.
- What are the risks of central bank intervention in the Forex market? While central bank interventions can stabilize the currency, they can also lead to market distortions or excessive reliance on artificial support for the currency. Over time, frequent or unpredictable interventions may reduce investor confidence, leading to increased market volatility or potential long-term impacts on India’s trade and investment environment.
Get It Touch
Error: Contact form not found.





