AUTHOR : SIMON DRAVIS
Introduction
The Forex (Foreign Exchange) market is a vast and intricate system where currencies are traded globally[1]. For anyone involved in Forex trading[2], understanding market cycles is critical to making informed trading decisions. In this article, we will explore various market cycle theories that can help traders understand the ebbs and flows of the Forex market, especially within the Indian context.
Understanding Forex Market Cycles
A Forex market[3] cycle is the movement of currency prices through a consistent, repetitive pattern. These cycles occur over different time frames and are driven by various factors, including economic data, geopolitical events, market sentiment, and interest rates. Understanding these cycles can give traders a strategic edge, allowing them to predict price movements and make informed trades.
Market cycles[4] in Forex can be broken down into several phases:
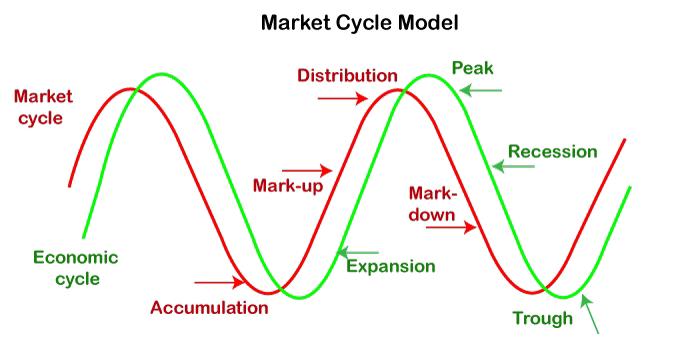
- Accumulation
- Mark-up
- Distribution
- Mark-down
The Accumulation Phase
The accumulation phase represents a period where the market is in a consolidation or sideways movement. This phase occurs after a significant downward trend. At this stage, prices tend to stabilize, and large institutional traders[5] begin to accumulate positions in anticipation of an upcoming upward trend. The public or smaller retail traders typically stay on the sidelines as they are not yet convinced that a reversal is happening. However, the early signs of a potential trend reversal start to take shape, and experienced traders begin to prepare for the next phase.
The Mark-up Phase
Once the accumulation phase ends, the mark-up phase begins. This is the period of a strong upward movement in the market. The buying interest grows significantly as the price begins to rise, attracting more traders and investors. Many Forex traders begin to enter the market at this point, and this phase is marked by an increasing trend. During this phase, a rise in economic indicators or changes in central bank policies (such as rate hikes) could support the trend further, particularly in the Indian market, where policy changes often affect currency values.
The Distribution Phase
The distribution phase is where the market starts to show signs of topping out. After a prolonged uptrend, institutional traders begin to take profits, selling off their accumulated positions. At this stage, prices may continue to rise but at a slower pace. Retail traders who were caught up in the excitement of the mark-up phase may continue buying, unaware that the trend is nearing its end. The distribution phase signals that the market is ready for a reversal, often followed by a downturn.
The Mark-down Phase
The mark-down phase is where the market begins its downward movement. After the distribution phase, prices fall as the selling pressure outweighs the buying pressure. Traders who bought during the distribution phase may panic and exit their positions, further contributing to the price decline. The market moves in a downward cycle until it hits another accumulation phase, where the cycle begins again. The mark-down phase can be triggered by negative economic data, geopolitical uncertainty, or central bank interventions.
Market Cycle Theories and Their Application in India
In India, Forex trading is heavily influenced by macroeconomic factors such as inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical events. Traders need to be aware of these factors as they can impact the Indian Rupee (INR) and other foreign currencies traded in the market. Some of the popular market cycle theories used by Forex traders in India include:
1. Elliott Wave Theory
The Elliott Wave Theory, developed by Ralph Nelson Elliott in the 1930s, suggests that market movements follow a predictable wave pattern. According to the theory, price movements in the market move in five waves in the direction of the trend (impulse waves), followed by three waves in the opposite direction (corrective waves).
In the context of Forex trading in India, the Elliott Wave Theory can be applied to predict potential price moves of the Indian Rupee against major currencies like the US Dollar (USD), Euro (EUR), and others. Understanding these waves helps traders identify entry and exit points, as well as the best times to trade during different phases of the market cycle.
2. Dow Theory
The Dow Theory, introduced by Charles Dow, is one of the oldest and most widely used market cycle theories. It emphasizes that the market moves in trends, and these trends are driven by factors such as economic conditions, interest rates, and corporate earnings. According to the Dow Theory, the market goes through three types of trends: primary trends, secondary trends, and minor trends.
In the Indian Forex market, traders can use the Dow Theory to identify long-term and short-term trends for the Indian Rupee. For instance, if the Indian economy is growing, it could trigger an upward trend in the INR against major currencies. Conversely, if the Indian economy is facing challenges, it could lead to a downward trend.
3. The Kondratieff Wave
The Kondratieff Wave theory, developed by Russian economist Nikolai Kondratieff, suggests that long-term economic cycles (lasting 40-60 years) play a significant role in driving market movements. These waves are divided into four phases: expansion, stagnation, recession, and recovery.
In the Indian Forex market, the Kondratieff Wave theory could help traders understand the long-term economic cycles that influence the value of the Indian Rupee. For example, the Indian economy may go through a period of expansion, leading to a strengthening of the INR against other currencies. Conversely, during a recessionary phase, the INR might weaken due to reduced investor confidence.
Key Factors Influencing Forex Cycles in India
Several factors affect the Forex market cycle, particularly in India. These include:
1. Interest Rates and Central Bank Policies
In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays a significant role in influencing Forex cycles through its monetary policy. Changes in interest rates, quantitative easing, and other central bank actions directly impact the INR and other currencies. For example, when the RBI raises interest rates, it could strengthen the INR due to increased foreign investment.
2. Geopolitical Events
India’s political landscape, as well as global geopolitical events, can create significant volatility in the Forex market. Elections, changes in government policies, and international trade relations are some factors that can affect the value of the Indian Rupee. Political stability tends to support currency strength, while uncertainty can weaken the INR.
3. Global Economic Conditions
Global economic conditions such as inflation rates, economic growth, and commodity prices also influence Forex market cycles. As a major importer of oil, India’s currency can be significantly affected by changes in global oil prices. A rise in oil prices, for instance, could weaken the INR, leading to a bearish market cycle.
4. Market Sentiment
Sentiment plays a significant role in driving Forex market cycles. The psychology of traders can lead to market overreaction, especially during periods of high uncertainty. In India, factors such as stock market performance, inflation expectations, and investor sentiment towards emerging markets can lead to rapid shifts in the Forex cycle.
Conclusion
Understanding Forex market cycles is crucial for traders in India who want to navigate the dynamic and often unpredictable market. By applying various cycle theories, such as the Elliott Wave Theory, Dow Theory, and Kondratieff Wave, traders can predict potential price movements and make more informed decisions. Furthermore, being aware of the factors that influence the Indian Forex market, such as interest rates, geopolitical events, and global economic conditions, will help traders better understand the cyclical behavior of currency pairs.
FAQ
1. What are Forex market cycles?
Forex market cycles refer to the repetitive phases of price movements in the foreign exchange market. These phases include accumulation, mark-up, distribution, and mark-down.
2. How can I identify market cycles in Forex trading?
You can identify market cycles by observing price patterns, using technical analysis tools, and studying market indicators such as moving averages and oscillators.
3. What is the best market cycle theory for Forex trading in India?
There is no single “best” theory, but traders often use a combination of Elliott Wave Theory, Dow Theory, and Kondratieff Wave to understand market cycles. Each theory has its strengths, depending on the trader’s strategy and time frame.
4. How do central bank policies affect Forex cycles in India?
Central bank policies, such as interest rate decisions by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), play a significant role in determining the direction of the Indian Rupee and, consequently, the Forex market cycle.
5. Can geopolitical events impact Forex cycles in India?
Yes, geopolitical events such as elections, trade negotiations, and international relations can create volatility in the Forex market, affecting the Indian Rupee and contributing to market cycles.





